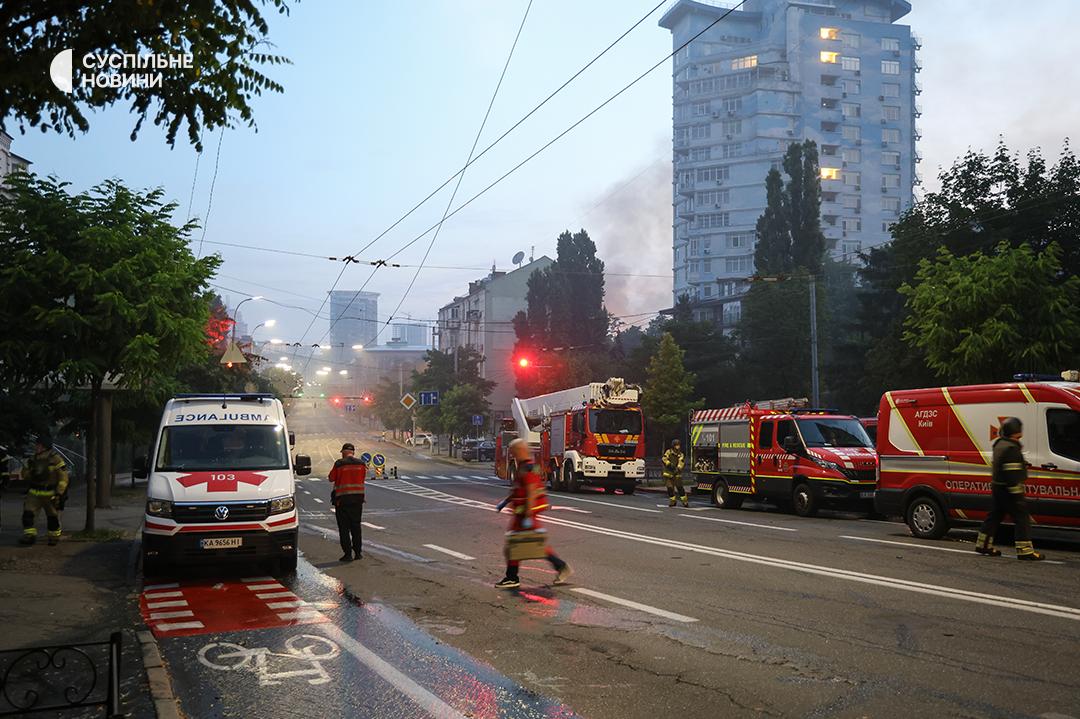
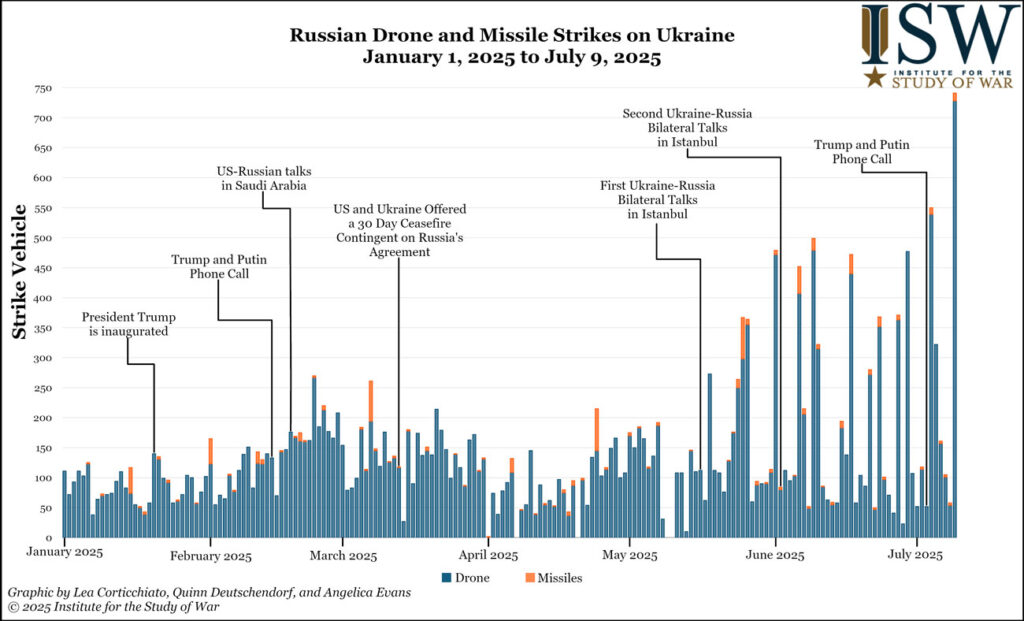
ISW: Russia is “burning the candle at both ends”—bankers quietly brace for bailouts

Russia is “burning the candle at both ends” economically as top bankers quietly brace for bailouts amid a growing Russian debt crisis, the Institute for the Study of War (ISW) wrote on 17 July. While the Kremlin pretends its economy is stable amid the ongoing protracted invasion of Ukraine, structural fractures continue to widen beneath that illusion.
Russian bankers brace for fallout as loans go unpaid
Bloomberg reported on 17 July that senior executives at several of Russia’s largest banks have quietly discussed the possibility of requesting government bailouts. This comes as non-performing loans — debts that are late or unpaid — continue to rise in 2025. Documents reviewed by Bloomberg show that three systemically important Russian banks may need to recover funds lost to bad credit.
Russian banks have already seen non-performing loans grow by 1.2% this year. Forecasts suggest the rate could increase from the current 4% to as high as 6–7% by 2026. While ISW cannot independently verify these figures, it notes mounting signs of concern within the financial sector.
Central Bank Chairperson Elvira Nabiullina has dismissed fears of a banking crisis, claiming that reserves totaling eight trillion rubles (around $102.5 billion) are sufficient to cushion any shocks. However, ISW assesses that the Central Bank is likely unwilling to bail out major banks outright — a decision that could spark liquidity problems or even bank failures, directly undermining Russian President Vladimir Putin’s narrative of economic resilience.
War-driven spending pressures the economy
ISW argues that the Kremlin is worsening the growing Russian debt crisis by expanding military spending while relaxing monetary policy to support short-term growth. Since 2022, the government has boosted one-time payments and salaries to attract military recruits and reinforce its defense industrial base. These high payments are necessary due to sustained battlefield losses and the challenge of attracting volunteers.
As defense wages rise, civilian industries struggle to retain workers, pushing up prices across service sectors. Labor shortages now impact both economic growth and war production. ISW maintains that Russia cannot indefinitely sustain these payouts or replace troops lost at current rates without a general mobilization — a step Putin has avoided.
Inflation appears tamed — but only on paper
On the surface, the Russian Central Bank reports success in reducing inflation. Bloomberg noted that in June 2025, the seasonally adjusted annual rate (SAAR) of inflation fell to 4%, matching the Bank’s target. The drop is attributed in part to a temporarily strong ruble, which lowered the cost of imported goods and helped suppress input costs and inflationary pressures for companies.
However, the Central Bank acknowledged that official annual inflation still stands at 9%. The SAAR is a short-term measure and does not reflect deeper economic trends. ISW argues that this data masks the real problems. Two complicating factors — the fading effect of ruble strength and rising service costs — are expected to slow progress in bringing inflation under control.
Contradictions threaten long-term stability
The think tank concludes wrote:
“Russia is effectively burning the candle at both ends by simultaneously loosening monetary policy to stimulate short-term growth, while expanding fiscal expenditure to feed the military effort.”
This path is likely to deepen the country’s macroeconomic instability, erode the value of the ruble, and diminish consumers’ ability to cope with rising costs. Behind the Central Bank’s controlled narrative, ISW sees rising stress in Russia’s economic foundation — a crisis building quietly but steadily.
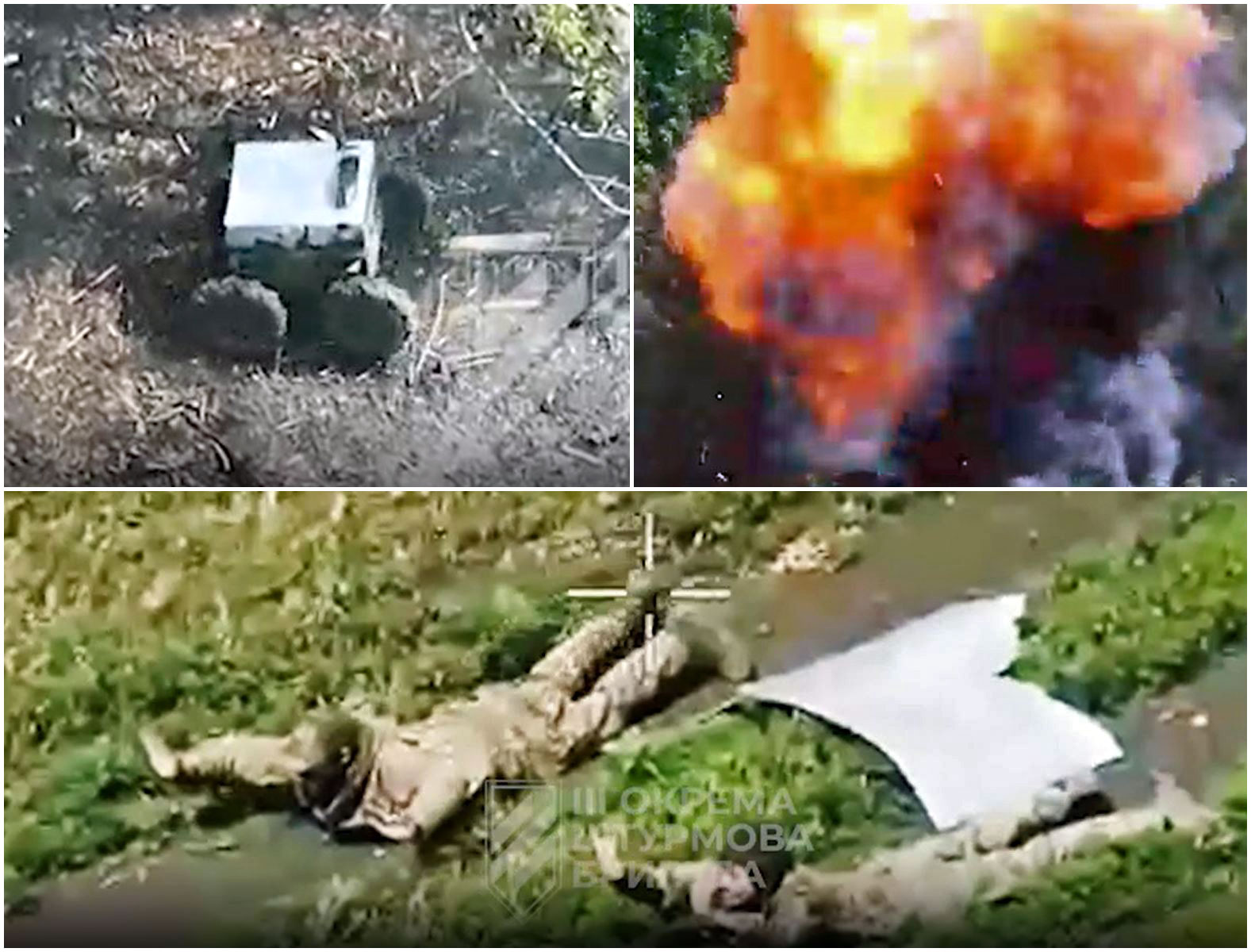
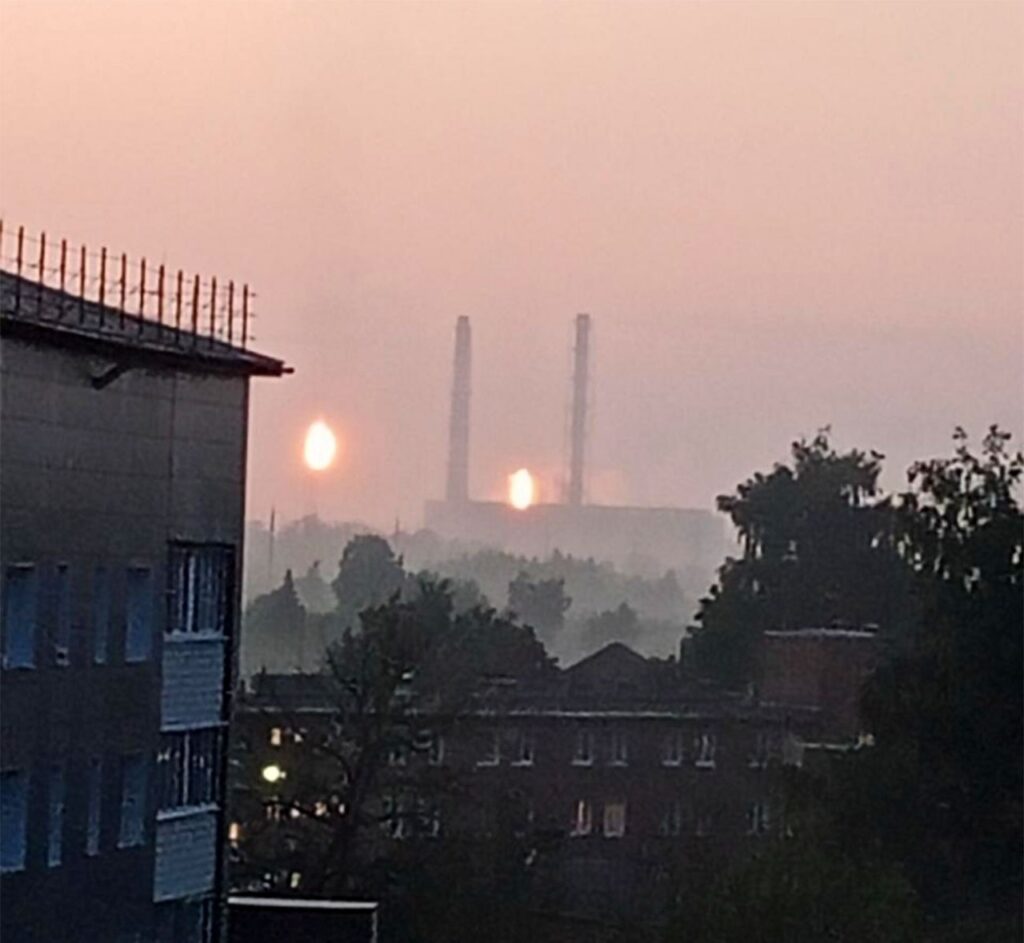



















 #1-3 Tula, #4 Roslavl, by TG/Supernova+
#1-3 Tula, #4 Roslavl, by TG/Supernova+ 
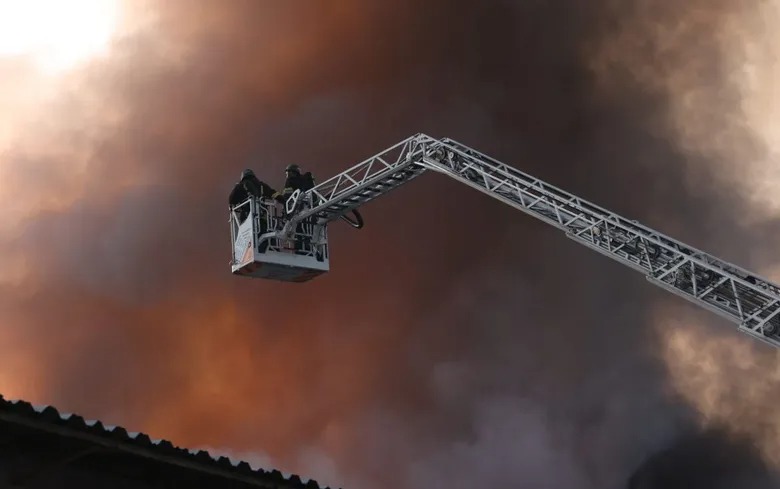
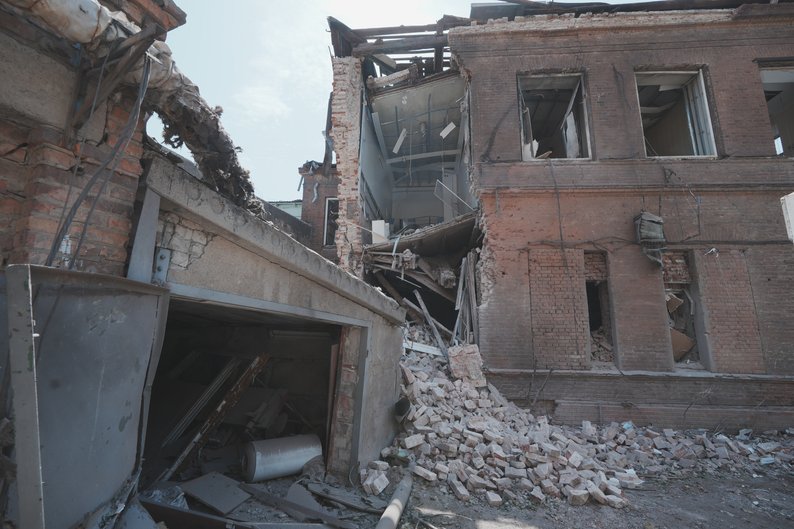
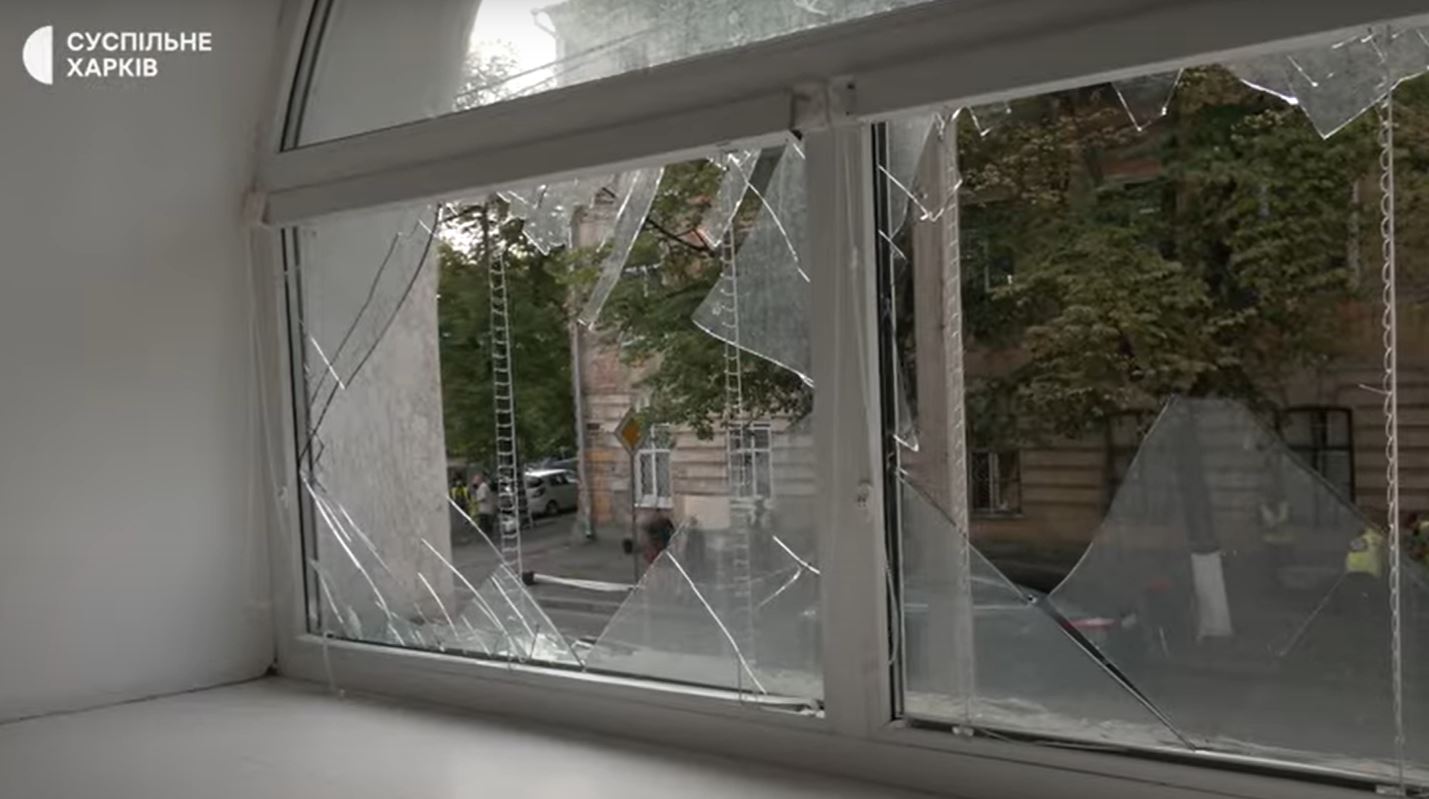
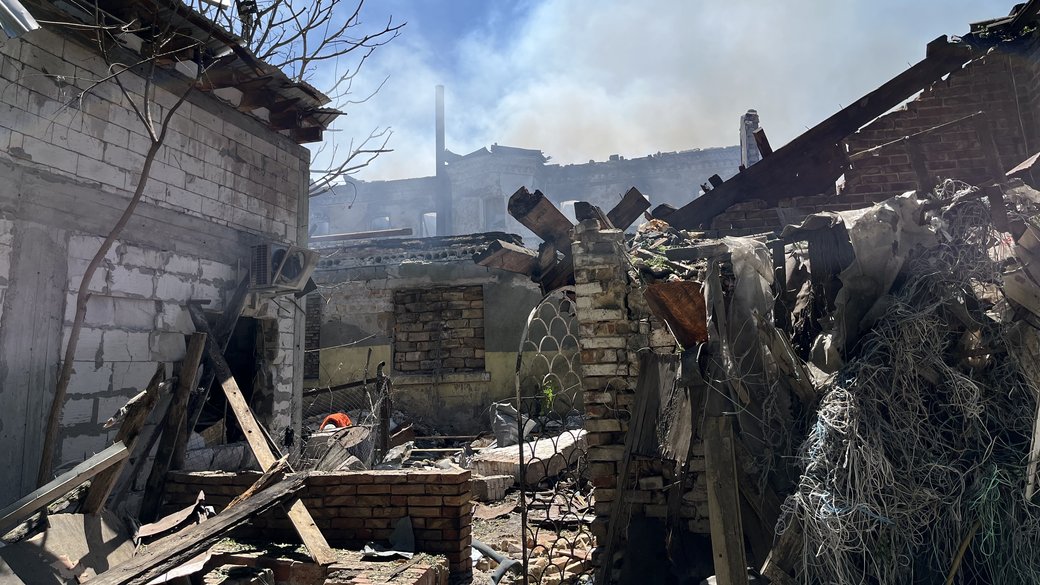
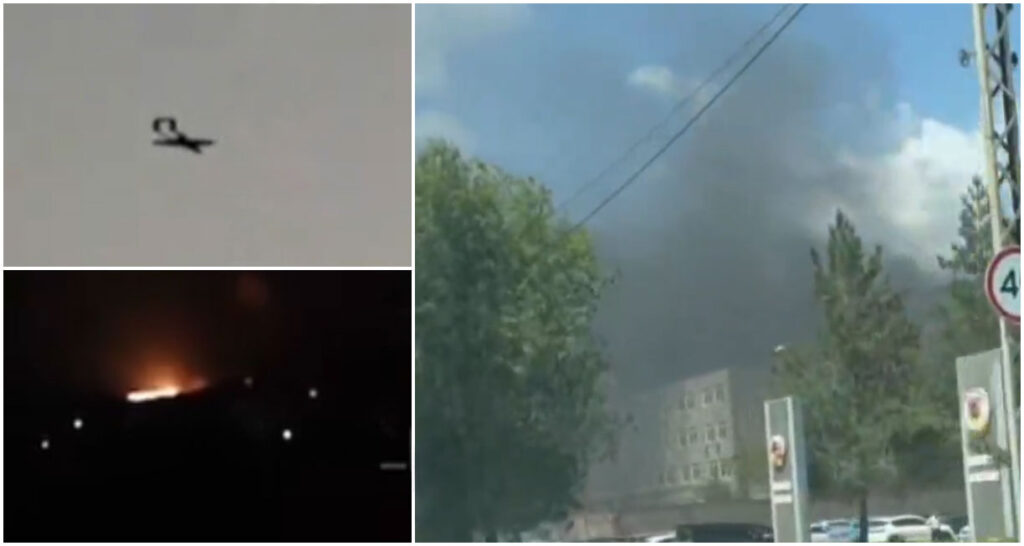























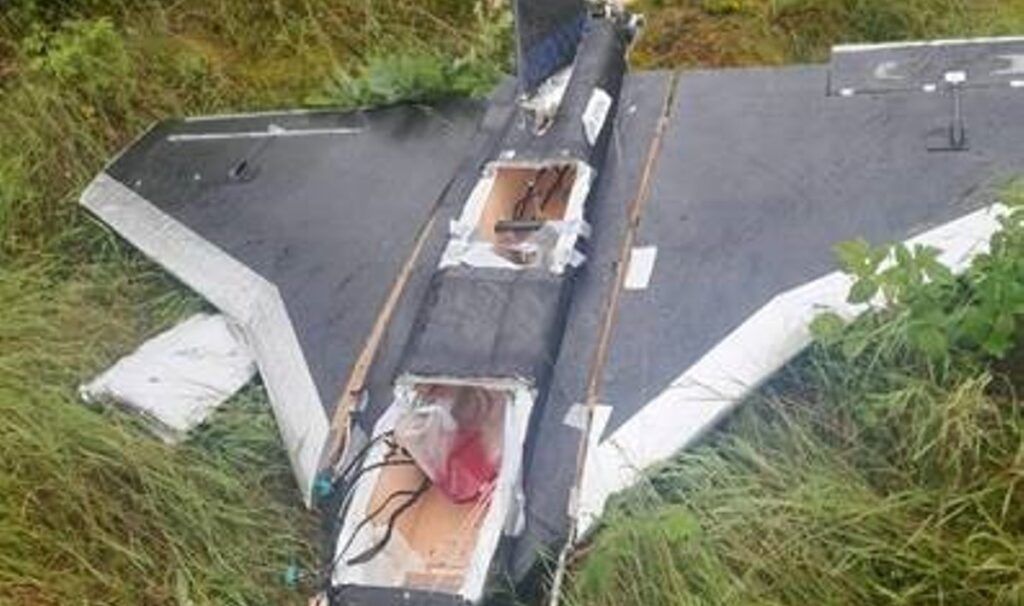
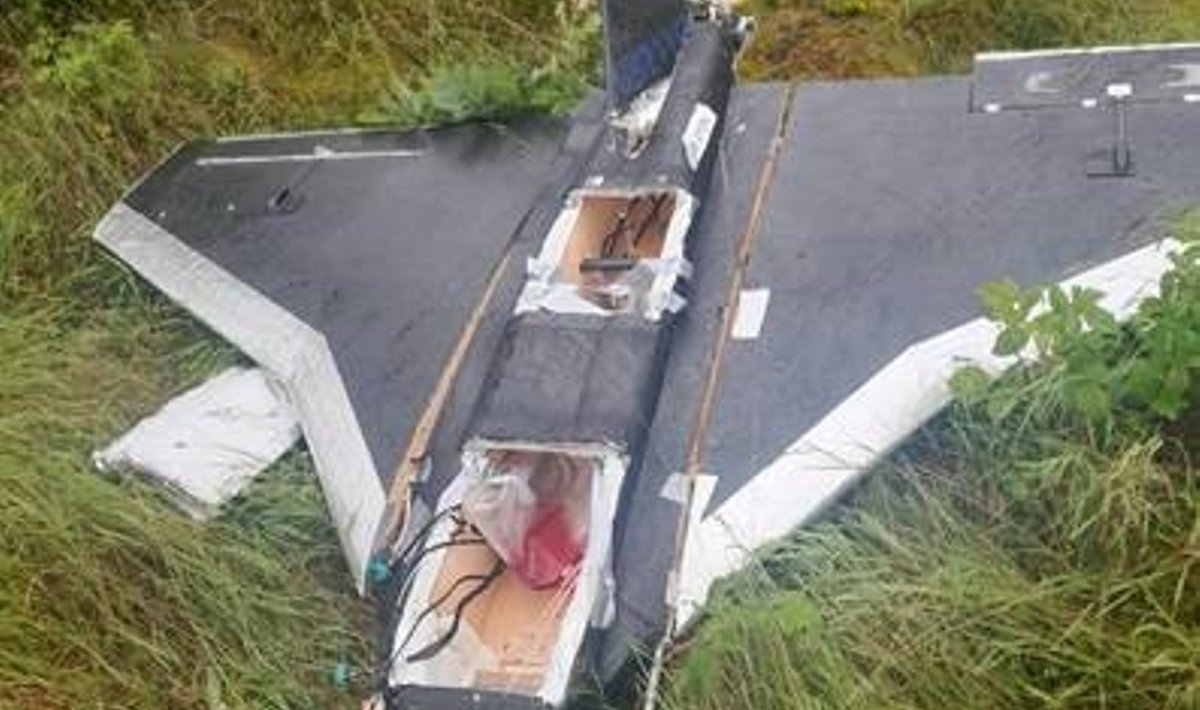
 Lukhovitsy (Moscow Oblast): Ukrainian Liutyi drones reportedly struck the Lukhovitsky Aviation Plant, part of the MiG aircraft corporation. Astra said two drones hit a compressor station, causing partial collapse of one wall.
Lukhovitsy (Moscow Oblast): Ukrainian Liutyi drones reportedly struck the Lukhovitsky Aviation Plant, part of the MiG aircraft corporation. Astra said two drones hit a compressor station, causing partial collapse of one wall.