Vue lecture
120 secondes de Tech / 16 sept 2025
Le Sénat américain confirme la nomination à la Fed du conseiller de Donald Trump Stephen Miran

TikTok devrait passer sous pavillon américain après un accord Chine-États-Unis

120 secondes de Tech / 15 sept 2025
"L'incertitude n'est jamais une bonne variable" : la note française rétrogradée par l'agence Fitch ?

L'agence Fitch se penche sur la dette souveraine française et pourrait abaisser sa note

120 secondes de Tech / 12 sept 2025
Larry Ellison, le dinosaure de la tech qui dispute à Musk le titre d'homme le plus riche du monde

Qui est le géant ASML derrière la bonne fortune de la star française Mistral IA ?

120 secondes de Tech / 11 sept 2025
120 secondes de Tech / 10 sept 2025
120 secondes de Tech / 9 sept 2025
120 secondes de Tech / 8 sept 2025
120 secondes de Tech / 5 sept 2025
120 secondes de Tech / 4 sept 2025
120 secondes de Tech / 3 sept 2025
120 secondes de Tech / 2 sept 2025
120 secondes de Tech / 1er sept 2025
L'implant cérébral qui lit les pensées : miracle médical et nouvelles questions éthiques

120 secondes de Tech / 29 aout 2025
120 secondes de Tech / 28 aout 2025
120 secondes de Tech / 27 aout 2025
120 secondes de Tech / 26 aout 2025
120 secondes de Tech / 25 aout 2025
Quand la réalité virtuelle active le système immunitaire : coulisses d'une expérience scientifique

120 secondes de Tech / 22 aout 2025
120 secondes de Tech / 21 aout 2025
120 secondes de Tech / 20 aout 2025
120 secondes de Tech / 19 aout 2025
120 secondes de Tech / 18 aout 2025
“It’s a devil’s machine.”
Tech leaders say AI will bring us eternal life, help us spread out into the stars, and build a utopian world where we never have to work. They describe a future free of pain and suffering, in which all human knowledge will be wired into our brains. Their utopian promises sound more like proselytizing than science, as if AI were the new religion and the tech bros its priests. So how are real religious leaders responding?
As Georgia's first female Baptist bishop, Rusudan Gotsiridze challenges the doctrines of the Orthodox Church, and is known for her passionate defence of women’s and LGBTQ+ rights. She stands at the vanguard of old religion, an example of its attempts to modernize — so what does she think of the new religion being built in Silicon Valley, where tech gurus say they are building a superintelligent, omniscient being in the form of Artificial General Intelligence?
Gotsiridze first tried to use AI a few months ago. The result chilled her to the bone. It made her wonder if Artificial Intelligence was in fact a benevolent force, and to think about how she should respond to it from the perspective of her religious beliefs and practices.
In this conversation with Coda’s Isobel Cockerell, Bishop Gotsiridze discusses the religious questions around AI: whether AI can really help us hack back into paradise, and what to make of the outlandish visions of Silicon Valley’s powerful tech evangelists.

This conversation took place at ZEG Storytelling Festival in Tbilisi in June 2025. It has been lightly edited and condensed for clarity.
Isobel: Tell me about your relationship with AI right now.
Rusudan: Well, I’d like to say I’m an AI virgin. But maybe that’s not fully honest. I had one contact with ChatGPT. I didn’t ask it to write my Sunday sermon. I just asked it to draw my portrait. How narcissistic of me. I said, “Make a portrait of Bishop Rusudan Gotsiridze.” I waited and waited. The portrait looked nothing like me. It looked like my mom, who passed away ten years ago. And it looked like her when she was going through chemo, with her puffy face. It was really creepy. So I will think twice before asking ChatGPT anything again. I know it’s supposed to be magical... but that wasn’t the best first date.

Isobel: What went through your mind when you saw this picture of your mother?
Rusudan: I thought, “Oh my goodness, it’s really a devil’s machine.” How could it go so deep? Find my facial features and connect them with someone who didn’t look like me? I take more after my paternal side. The only thing I could recognize was the priestly collar and the cross. Okay. Bishop. Got it. But yes, it was really very strange.
Isobel: I find it so interesting that you talk about summoning the dead through Artificial Intelligence. That’s something happening in San Francisco as well. When I was there last summer, we heard about this movement that meets every Sunday. Instead of church, they hold what they call an “AI séance,” where they use AI to call up the spirit world. To call up the dead. They believe the generative art that AI creates is a kind of expression of the spirit world, an expression of a greater force.
They wouldn’t let us attend. We begged, but it was a closed cult. Still, a bunch of artists had the exact same experience you had: they called up these images and felt like they were summoning them, not from technology, but from another realm.
Rusudan: When you’re a religious person dealing with new technologies, it’s uncomfortable. Religion — Christianity, Protestantism, and many others — has earned a very cautious reputation throughout history because we’ve always feared progress.
Remember when we thought printing books was the devil’s work? Later, we embraced it. We feared vaccinations. We feared computers, the internet. And now, again, we fear AI.
It reminds me of the old proverb about a young shepherd who loved to prank his friends by shouting “Wolves! Wolves!” until one day, the wolves really came. He shouted, but no one believed him anymore.
We’ve been shouting “wolves” for centuries. And now, I’m this close to shouting it again, but I’m not sure.
Isobel: You said you wondered if this was the devil’s work when you saw that picture of your mother. It’s quite interesting. In Silicon Valley, people talk a lot about AI bringing about the rapture, apocalypse, hell.
They talk about the real possibility that AI is going to kill us all, what the endgame or extinction risk of building superintelligent models will be. Some people working in AI are predicting we’ll all be dead by 2030.
On the other side, people say, “We’re building utopia. We’re building heaven on Earth. A world where no one has to work or suffer. We’ll spread into the stars. We’ll be freed from death. We’ll become immortal.”
I’m not a religious person, but what struck me is the religiosity of these promises. And I wanted to ask you — are we hacking our way back into the Garden of Eden? Should we just follow the light? Is this the serpent talking to us?
Rusudan: I was listening to a Google scientist. He said that in the near future, we’re not heading to utopia but dystopia. It’s going to be hell on Earth. All the world’s wealth will be concentrated in a small circle, and poverty will grow. Terrible things will happen, before we reach utopia.
Listening to him, it really sounded like the Book of Revelation. First the Antichrist comes, and then Christ.
Because of my Protestant upbringing, I’ve heard so many lectures about the exact timeline of the Second Coming. Some people even name the day, hour, place. And when those times pass, they’re frustrated. But they carry on calculating.
It’s hard for me to speak about dystopia, utopia, or the apocalyptic timeline, because I know nothing is going to be exactly as predicted.
The only thing I’m afraid of in this Artificial Intelligence era is my 2-year-old niece. She’s brilliant. You can tell by her eyes. She doesn’t speak our language yet. But phonetically, you can hear Georgian, English, Russian, even Chinese words from the reels she watches non-stop.
That’s what I’m afraid of: us constantly watching our devices and losing human connection. We’re going to have a deeply depressed young generation soon.
I used to identify as a social person. I loved being around people. That’s why I became a priest. But now, I find it terribly difficult to pull myself out of my house to be among people. And it’s not just a technology problem — it’s a human laziness problem.
When we find someone or something to take over our duties, we gladly hand them over. That’s how we’re using this new technology. Yes, I’m in sermon mode now — it’s a Sunday, after all.
I want to tell you an interesting story from my previous life. I used to be a gender expert, training people about gender equality. One example I found fascinating: in a Middle Eastern village without running water, women would carry vessels to the well every morning and evening. It was their duty.
Western gender experts saw this and decided to help. They installed a water supply. Every woman got running water in her kitchen: happy ending. But very soon, the pipeline was intentionally broken by the women. Why? Because that water-fetching routine was the only excuse they had to leave their homes and see their friends. With running water, they became captives to their household duties.
One day, we may also not understand why we’ve become captives to our own devices. We’ll enjoy staying home and not seeing our friends and relatives. I don’t think we’ll break that pipeline and go out again to enjoy real life.
Isobel: It feels like it’s becoming more and more difficult to break that pipeline. It’s not really an option anymore to live without the water, without technology.
Sometimes I talk with people in a movement called the New Luddites. They also call themselves the Dumbphone Revolution. They want to create a five-to-ten percent faction of society which doesn’t have a smartphone, and they say that will help us all, because it will mean the world will still have to cater to people who don’t participate in big tech, who don’t have it in their lives. But is that the answer for all of us? To just smash the pipeline to restore human connection? Or can we have both?
Rusudan: I was a new mom in the nineties in Georgia. I had two children at a time when we didn’t have running water. I had to wash my kids’ clothes in the yard in cold water, summer and winter. I remember when we bought our first washing machine. My husband and I sat in front of it for half an hour, watching it go round and round. It was paradise for me for a while.
Now this washing machine is there and I don't enjoy it anymore. It's just a regular thing in my life. And when I had to wash my son’s and daughter-in-law’s wedding outfits, I didn’t trust the machine. I washed those clothes by hand. There are times when it’s important to do things by hand.
Of course, I don’t want to go back to a time without the internet when we were washing clothes in the yard, but there are things that are important to do without technology.
I enjoy painting, and I paint quite a lot with watercolors. So far, I can tell which paintings are AI and which are real. Every time I look at an AI-made watercolour, I can tell it’s not a human painting. It is a technological painting. And it's beautiful. I know I can never compete with this technology.
But that feeling, when you put your brush in, the water — sometimes I accidentally put it in my coffee cup — and when you put that brush on the paper and the pigment spreads, that feeling can never be replaced by any technology.
Isobel:
As a writer, I'm now pretty good, I think, at knowing if something is AI-written or not. I'm sure in the future it will get harder to tell, but right now, there are little clues. There’s this horrible construction that AI loves: something is not just X, it’s Y. For example: “Rusudan is not just a bishop, she’s an oracle for the LGBTQ community in Georgia.” Even if you tell it to stop using that construction, it can’t. Same for the endless em-dashes: I can’t get ChatGPT to stop using them no matter how many times or how adamantly I prompt it. It's just bad writing.
It’s missing that fingerprint of imperfection that a human leaves: whether it’s an unusual sentence construction or an interesting word choice, I’ve started to really appreciate those details in real writing. I've also started to really love typos. My whole life as a journalist I was horrified by them. But now when I see a typo, I feel so pleased. It means a human wrote it. It’s something to be celebrated. It’s the same with the idea that you dip your paintbrush in the coffee pot and there’s a bit of coffee in the painting. Those are the things that make the work we make alive.
There’s a beauty in those imperfections, and that’s something AI has no understanding of. Maybe it’s because the people building these systems want to optimize everything. They are in pursuit of total perfection. But I think that the pursuit of imperfection is such a beautiful thing and something that we can strive for.
Rusudan: Another thing I hope for with this development of AI is that it’ll change the formula of our existence. Right now, we’re constantly competing with each other. The educational system is that way. Business is that way. Everything is that way. My hope is that we can never be as smart as AI. Maybe one day, our smartness, our intelligence, will be defined not by how many books we have read, but by how much we enjoy reading books, enjoy finding new things in the universe, and how well we live life and are happy with what we do. I think there is potential in the idea that we will never be able to compete with AI, so why don’t we enjoy the book from cover to cover, or the painting with the coffee pigment or the paint? That’s what I see in the future, and I’m a very optimistic person. I suppose here you’re supposed to say “Halleluljah!”
Isobel: In our podcast, CAPTURED, we talked with engineers and founders in Silicon Valley whose dream for the future is to install all human knowledge in our brains, so we never have to learn anything again. Everyone will speak every language! We can rebuild the Tower of Babel! They talk about the future as a paradise. But my thought was, what about finding out things? What about curiosity? Doesn’t that belong in paradise? Certainly, as a journalist, for me, some people are in it for the impact and the outcome, but I’m in it for finding out, finding the story—that process of discovery.
Rusudan: It’s interesting —this idea of paradise as a place where we know everything. One of my students once asked me the same thing you just did. “What about the joy of finding new things? Where is that, in paradise?” Because in the Bible, Paul says that right now, we live in a dimension where we know very little, but there will be a time when we know everything.
In the Christian narrative, paradise is a strange, boring place where people dress in funny white tunics and play the harp. And I understand that idea back then was probably a dream for those who had to work hard for everything in their everyday life — they had to chop wood to keep their family warm, hunt to get food for the kids, and of course for them, paradise was the place where they just could just lie around and do nothing.
But I don’t think paradise will be a boring place. I think it will be a place where we enjoy working.
Isobel: Do you think AI will ever replace priests?
Rusudan: I was told that one day there will be AI priests preaching sermons better than I do. People are already asking ChatGPT questions they’re reluctant to ask a priest or a psychologist. Because it’s judgment-free and their secrets are safe…ish. I don’t pretend I have all the answers because I don’t. I only have this human connection. I know there will be questions I cannot answer, and people will go and ask ChatGPT. But I know that human connection — the touch of a hand, eye-contact — can never be replaced by AI. That’s my hope. So we don’t need to break those pipelines. We can enjoy the technology, and the human connection too.
This conversation took place at ZEG Storytelling Festival in Tbilisi in June 2025.
Your Early Warning System
This story is part of “Captured”, our special issue in which we ask whether AI, as it becomes integrated into every part of our lives, is now a belief system. Who are the prophets? What are the commandments? Is there an ethical code? How do the AI evangelists imagine the future? And what does that future mean for the rest of us? You can listen to the Captured audio series on Audible now.
Related Articles
The Vatican challenges AI’s god complex
Pope Francis’s final warning
When I’m 125?
The post “It’s a devil’s machine.” appeared first on Coda Story.
Ukrainian-founded Grammarly to acquire AI email app Superhuman

Grammarly, a company with Ukrainian roots, announced its intent to acquire AI email writing app Superhuman as part of its expansion into an AI productivity platform, the company said in a press release on July 1.
Grammarly is the most valuable company with Ukrainian roots, reaching $13 billion valuation as of 2021. Grammarly was founded in 2009 in Kyiv by Oleksii Shevchenko, Maksym Lytvyn, and Dmytro Lider.
According to Grammarly's press release, email is Grammarly's top use case, with the platform editing over 50 million emails weekly.
Superhuman is an AI email application that the company says helps users respond to emails faster and reduces time spent on email communications.
Users are already sending and responding to 72% more emails per hour after using Superhuman compared to the previous period, according to Grammarly.
"This is the future we've been building toward since day one: AI that works where people work, not where companies want them to work," said Shishir Mehrotra, Grammarly's CEO.
The acquisition follows Grammarly's recent purchase of Coda, a productivity tool company. The combined platforms will allow users to work with multiple AI agents for different tasks within email communications.
Grammarly says that its service is used daily by over 40 million users, generating annual revenue of more than $700 million for the company.
 The Kyiv IndependentAbbey Fenbert
The Kyiv IndependentAbbey Fenbert
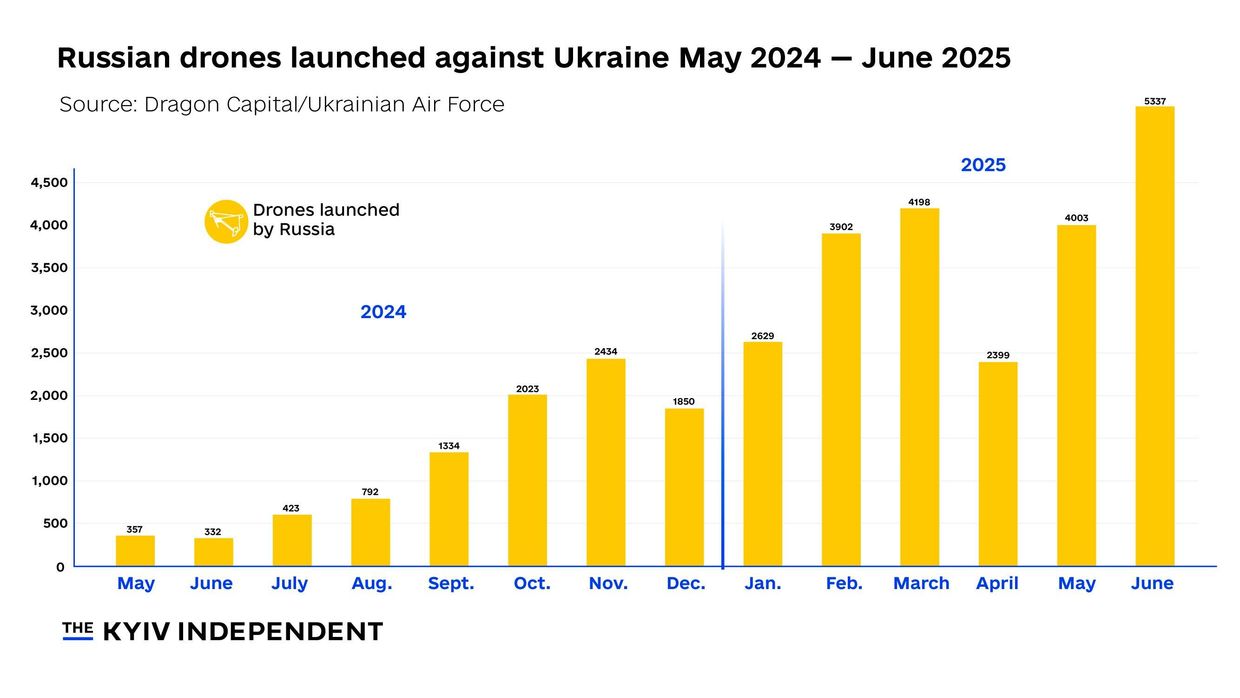
Russia cannot launch 500 drones every day, Ukraine's intel chief says
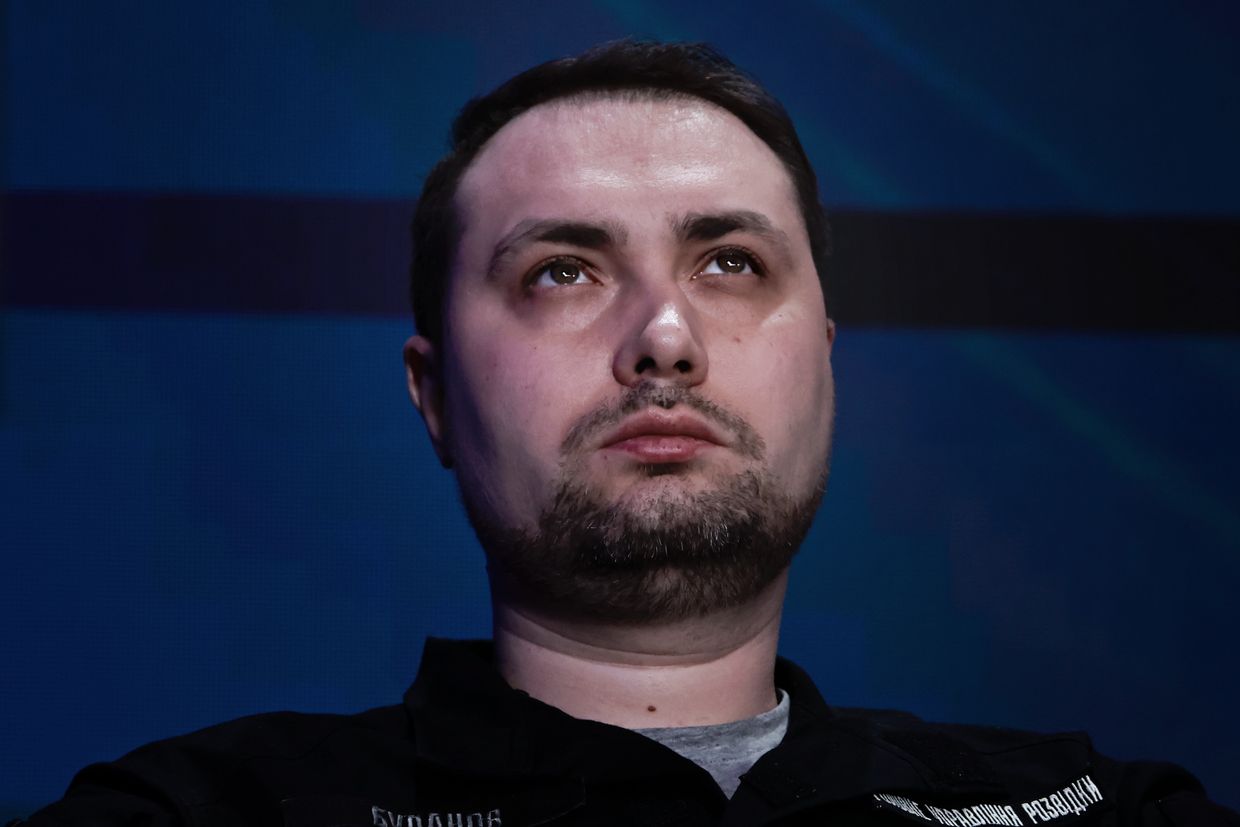

Russia has the capacity to launch as many as 500 Iranian-designed Shahed attack drones at Ukraine in a single attack, but doing so on a daily basis is not possible, Ukraine's military intelligence chief Kyrylo Budanov said on July 2, according to Suspilne.
In recent weeks, Russia has intensified its drone assaults on Ukrainian cities, often launching hundreds in a single day. The largest aerial attack since the start of the full-scale invasion occurred overnight on June 29, when Moscow launched 477 drones and 60 missiles across Ukraine.
"Launching 450–500 Shaheds every day — it's just not realistic," said Budanov during a ceremony recognizing five Ukrainian intelligence achievements in the national record book, according to public broadcaster Suspilne.
"But unfortunately, they do have the ability to do it periodically. They can realistically launch up to 500 in one strike," Budanov added.
Budanov also said Russia is upgrading the capabilities of the Shahed-type drones by improving their CRPA (Controlled Reception Pattern Antenna) systems, which protect the drones from GPS jamming. He noted that Russian engineers are now producing 16-channel CRPA antennas, which are harder to counter electronically.
"These antennas are currently produced in Russia, but the engineer who developed this CRPA antenna was here in Ukraine," Budanov said.
"Back in the early 2000s, no one here needed it, so the engineer moved to Russia. One (of the two engineers involved in the development) has already died under unclear circumstances. The other is still alive, though probably not for long."
Russia has used thousands of Shahed-type drones throughout its full-scale invasion to strike Ukrainian cities and infrastructure, often in large overnight waves. Ukrainian air defenses have adapted over time but face growing challenges as Moscow improves drone resilience and electronic warfare capabilities.
President Volodymyr Zelensky said that Moscow has launched 28,743 Shahed-type drones at Ukraine since the start of Russia's full-scale invasion.
Budanov also said Russia has made unsuccessful attempts to develop its own naval drones. The last known effort came in early June, when experimental models detonated before reaching Ukrainian territorial waters, he said.
"They didn't achieve results. Based on our information, they were heading toward the city of Yuzhne, searching for targets," he said.
Ukraine has been using domestically developed Magura naval drones to target Russian military assets in the Black Sea, keeping much of Russia's fleet pinned in port.
Despite their small size, the unmanned surface vessels have proven effective, including in a May 2 operation when Ukraine's military intelligence used Magura-7 drones armed with air-to-air missiles to shoot down two Russian Su-30 fighter jets near Novorossiysk. It was the first recorded instance of fighter jets being downed by naval drones.
 The Kyiv IndependentMartin Fornusek
The Kyiv IndependentMartin Fornusek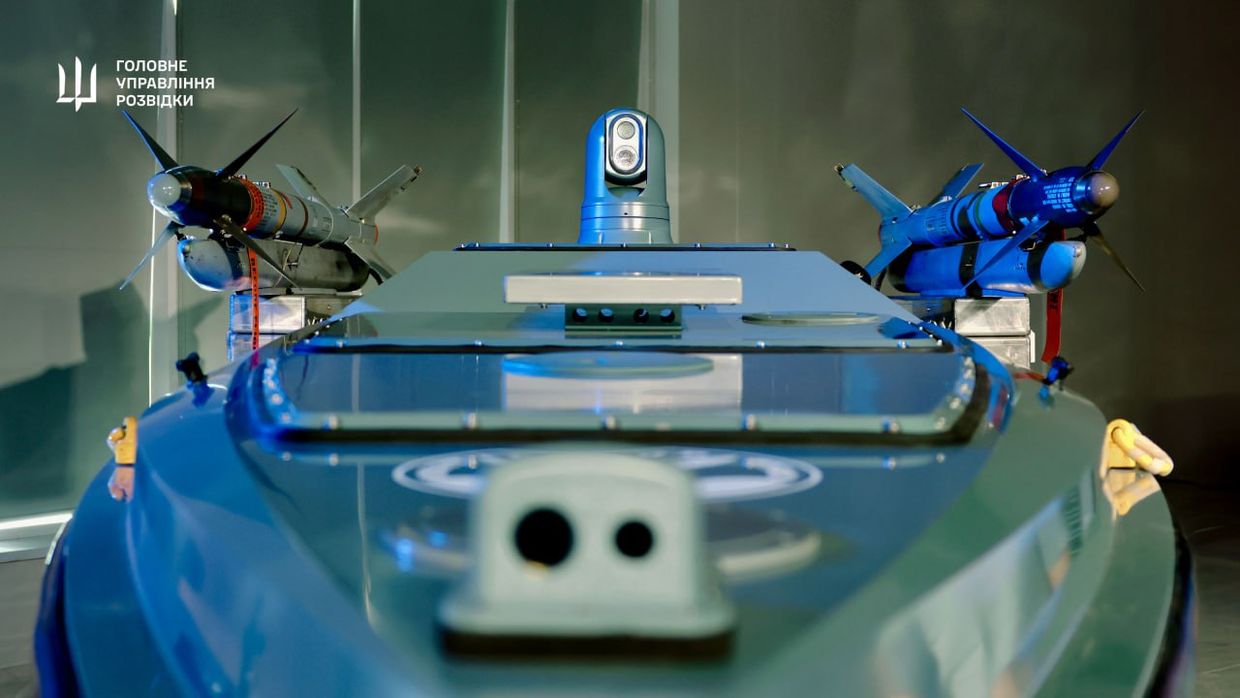
Ukraine approves new 'Murakha' ground robot for combat use
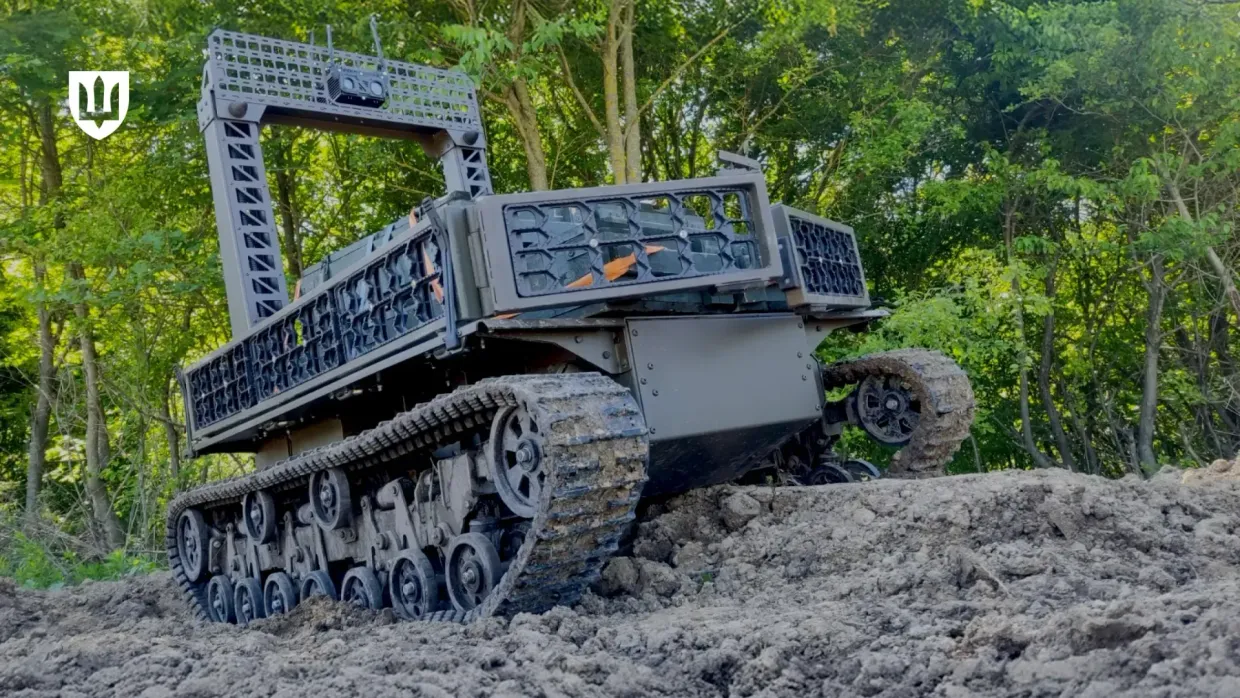

The Defense Ministry has approved the Ukrainian-made ground-based robotics complex "Murakha" ("Ant") for combat operations, the ministry announced on June 28.
Since 2024, Ukraine has been scaling up robotics development in hopes that mass production of unmanned ground vehicles (UGVs) will "minimize human involvement on the battlefield."
The Murakha is a tracked robotic platform designed to support front-line units working under challenging conditions, such as under enemy artillery and in heavily mined terrain, the Defense Ministry said.
Its larger size makes it one of Ukraine's leading UGVs in terms of load capacity. The Murakha can reportedly carry over half a ton of weight across dozens of kilometers. It can also cross difficult terrain and shallow water.
According to the Defense Ministry, the Murakha's multiple control channels allow it to function successfully even in areas of the battlefield where Russian electronic warfare (EW) systems are operating.
Mobile robots are capable of performing several tasks on the battlefield, including offensive and defensive activities, evacuation of the wounded, logistical support for units, and mining and demining.
In April, the Defense Ministry unveiled the D-21-12R UGV, a ground-based robot equipped with a machine gun.
 The Kyiv IndependentDmytro Basmat
The Kyiv IndependentDmytro Basmat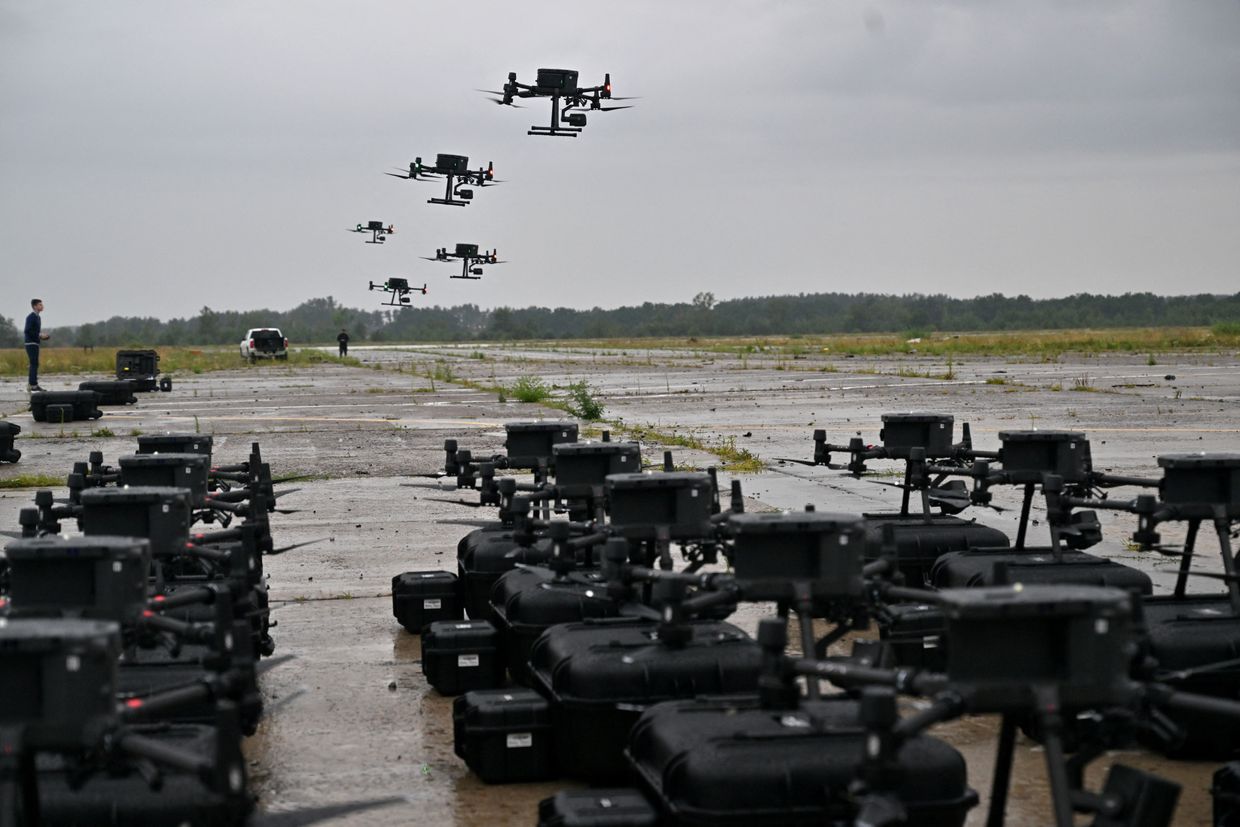
EU proposes integrating Ukraine into bloc's mobile roaming area

The European Commission has proposed that Ukraine join the European Union's mobile roaming area starting January 1, 2026, providing Ukrainian users the ability to make phone calls, texts, and use mobile data in the bloc's 27 countries at no extra charge.
"We want Ukrainian citizens to stay connected to their loved ones across the EU, as well as in their home country. That's why we propose that Ukraine join our roaming family," European Commission President Ursula von der Leyen said in a statement.
The proposal, first announced on June 16, will serve as a means of integration into the European Union's "Roam like at Home" provision in affect between all EU nations. The proposed change will impact the over four million Ukrainian refugees living in the EU.
Ukraine's full integration in the roaming provisions will replace voluntary measures that "allowed for roaming without surcharges and affordable international calls for EU and Ukrainian citizens abroad," according to the European Commission. The current measure will extend to December 31, 2025, ahead of the planned integration.
If approved, Ukraine will become the only country outside of the EU to join the bloc's "Roam like at Home" policy.
The move, which awaits European Council approval, comes as Ukraine continues to implement reforms in pursuing membership in the European Union.
Ukraine applied for EU membership at the onset of Russia's full-scale invasion in 2022. The country has made quick progress, achieving candidate status within months, with the initial negotiations formally launching in June 2024.
Since the start of 2025, Ukraine has opened three negotiation clusters under Poland's rotating presidency.
Poland lead the EU Council's presidency until June, and Denmark will take over the role in July. Ukraine aims to open the remaining three negotiation clusters in the second half of 2025 under the Danish chairmanship, the President Volodymyr Zelensky said.
There are six accession negotiation clusters, consisting of several individual chapters. Negotiations prepare a candidate country to become an EU member.
The EU’s Commissioner for Enlargement, Oliver Varhelyi, said that Ukraine could potentially join the bloc by 2029 if it successfully implements necessary reforms.
 The Kyiv IndependentVolodymyr Ivanyshyn
The Kyiv IndependentVolodymyr Ivanyshyn
Welcome to the Technate
— Permalien


