NASA Rover Finds ‘Potential Biosignature’ on Mars

Welcome back to the Abstract! These are the studies this week that broke ice, broke hearts, and broke out the libations. Also, if you haven’t seen it already, we just covered an amazing breakthrough in our understanding of the cosmos, which is as much a story about humanity’s endless capacity for ingenuity as it is about the wondrous nature of black holes.
Microbes on ice
Scientists have discovered Arctic algae moving around with ease in icy environments of -15°C (5°F)—the lowest temperatures ever recorded for motility in a eukaryotic lifeform. While some simple microbes can survive lower temperatures, this is the first time that scientists have seen eukaryotic life—organisms with more complex cells containing a nucleus—able to live, thrive, and locomote in such chilly environments.
It’s amazing that these so-called “ice diatoms” can move around at all, but it’s even cooler that they do it in style with a gliding mechanism that researchers describe as a “‘skating’ ability.” Their secret weapon? Mucus threads (“mucilage”) that they use like anchors to pull themselves through frozen substrates.
“The unique ability of ice diatoms to glide on ice” enables them “to thrive in conditions that immobilize other marine diatoms,” said researchers led by Qing Zhang of Stanford University.
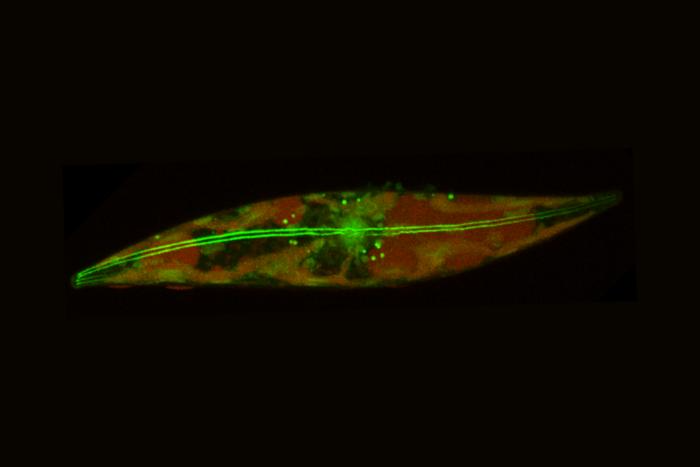
Zhang and her colleagues made this discovery by collecting ice cores from 12 locations around the Arctic Chukchi Sea during a 2023 expedition on the research vessel Sikuliaq, which is owned by the National Science Foundation (NSF) and operated by the University of Alaska Fairbanks. Unfortunately, this is a research area that could be destroyed by the Trump administration, with NSF facing 70 percent cuts to its polar research budget.
In other news…
How did Mars get its leopard spots?
If lifeforms are doing triple axels in Arctic ice on Earth, it’s natural to wonder whether alien organisms may have emerged elsewhere. To that end, scientists announced the discovery of a tantalizing hint of possible life on Mars this week.
NASA’s Perseverance rover turned up organic carbon-bearing mudstones that preserve past redox reactions, which involves the transfer of electrons between substances resulting in one being “reduced” (gaining electrons) and one being “oxidized” (losing electrons). The remnants of those reactions look like “leopard spots” in the Bright Angel formation of Jezero Crater, where the rover landed in 2021, according to the study.
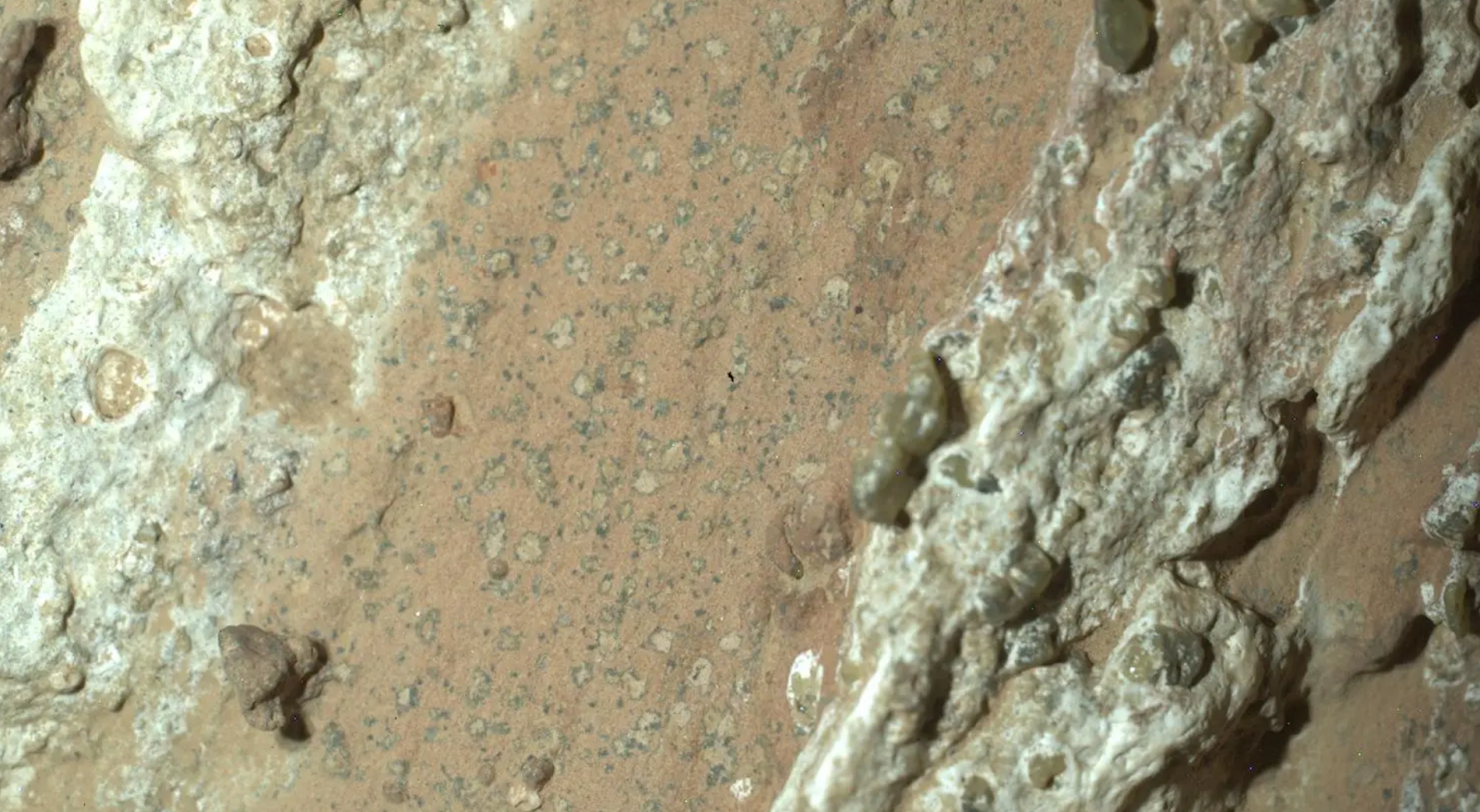

This is not slam-dunk evidence of life, as the reactions can be geological in origin, but they “warrant consideration as ‘potential biosignatures.”
“This assessment is further supported by the geological context of the Bright Angel formation, which indicates that it is sedimentary in origin and deposited from water under habitable conditions,” said researchers led by Joel Hurowitz of Stony Brook University.
The team added that the best way to confirm the origin of the ambiguous structures is to bring Perseverance’s samples back to Earth for further study as part of the Mars Sample Return (MSR) program. Unfortunately, the Trump administration wants to cancel MSR. It seems that even when we have nice things, we still can’t have nice things, a paradox that we all must navigate together.
The last flight of Lucky and Lucky II
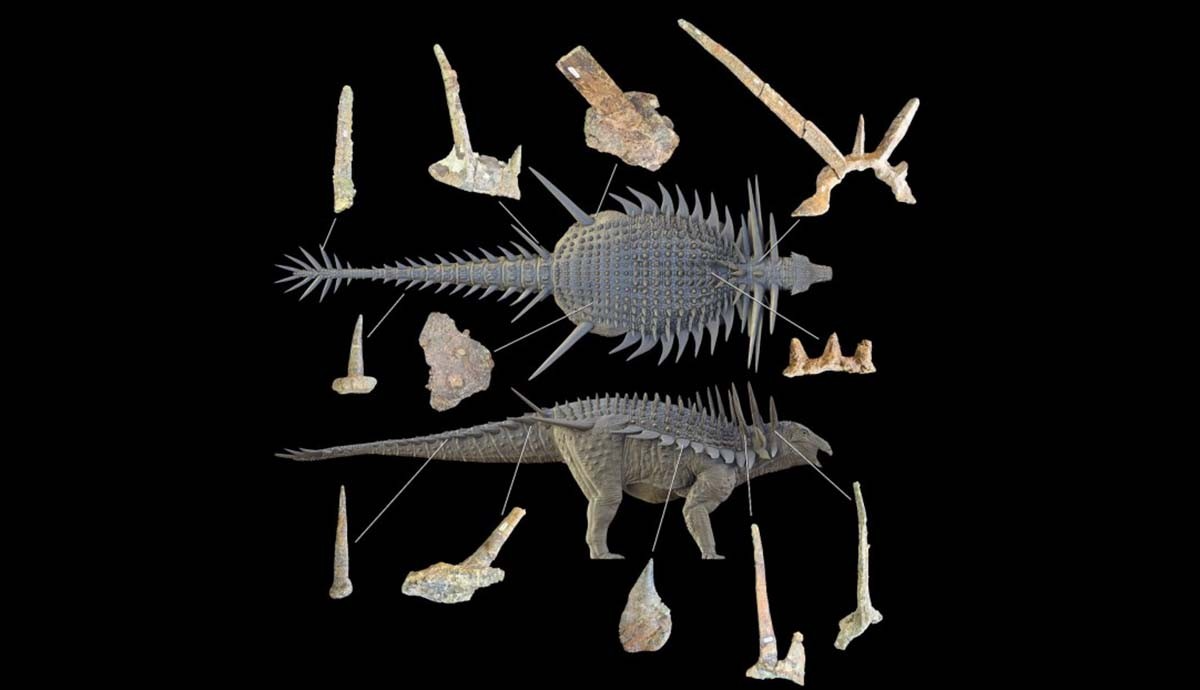
About 150 million years ago, a pair of tiny pterodactyls—just days or weeks old—were trying to fly through a cataclysmic storm. But the wind was strong enough to break the bones of their baby wings, consigning them to a watery grave in the lagoon below.
Now, scientists describe how the very storm that cut their lives short also set them up for a long afterlife as exquisitely preserved fossils, nicknamed Lucky and Lucky II, in Germany's Solnhofen limestone.
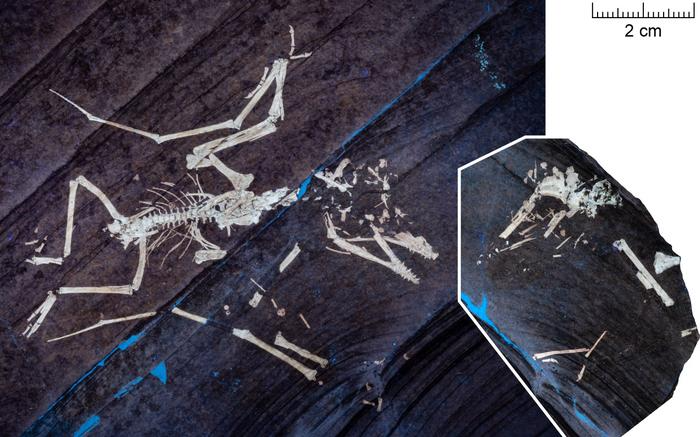

“Storms caused these pterosaurs to drown and rapidly descend to the bottom of the water column, where they were quickly buried in storm-generated sediments, preserving both their skeletal integrity and soft tissues,” said researchers led by Robert Smyth of the University of Leicester.
“This catastrophic taphonomic pathway, triggered by storm events, was likely the principal mechanism by which small- to medium-sized pterodactyloids…entered the Solnhofen assemblage,” they added.
While it’s sad that these poor babies had such short lives, it’s astonishing that such a clear cause of death can be established 150 million years later. Rest in peace, Lucky and Lucky II.
Trump’s aid cuts could cause millions of deaths from tuberculosis alone
The Trump administration’s gutting of the United States Agency for International Development (USAID), carried out in public fashion by Elon Musk and DOGE, will likely cause millions of excess deaths from tuberculosis (TB) by 2030, reports a sobering new study.
“Termination of US funding could result in an estimated 10.6 million additional TB cases and 2.2 million additional TB deaths during the period 2025–2030,” said researchers led by Sandip Mandal of the Center for Modeling and Analysis at Avenir Health. “The loss of U.S. funding endangers global TB control efforts” and “potentially puts millions of lives at risk.”
Beyond TB, the overall death toll from the loss of USAID is estimated to reach 14 million deaths by 2030. The destruction of USAID must never be memory-holed as it is shaping up to be among the most deadly actions ever enacted by a government outside of war.
Small microbes with big impacts
In more bad news, it turns out that the bacteria that’s responsible for making a lot of Earth’s oxygen is highly vulnerable to human-driven climate change. Prochlorococcus, the most abundant photosynthetic organism on Earth, is the source of about 20 percent of the oxygen in our biosphere. But rapidly warming seas could set off “a possible 17–51 percent reduction in Prochlorococcus production in tropical oceans,” according to a new study.
“Prochlorococcus division rates appear primarily determined by temperature, increasing exponentially to 28°C, then sharply declining,” said researchers led by François Ribalet of the University of Washington. “Regional surface water temperatures may exceed this range by the end of the century under both moderate and high warming scenarios.”
It’s possible that this vital bacteria will adapt by moving to higher latitudes or by evolving more heat-tolerant variants. But that seems like a big gamble on something as important as Earth’s oxygen budget.
Last, we feast
We are far from the first generation to live through unstable times, as evidenced by a new study about the “climatic change and economic upheaval” in Britain during the transition from the Bronze Age to the Iron Age about 3,000 years ago.
These disruptions were traumatic, but they also galvanized new modes of community connection—a.k.a epic parties where people ate, drank, made merry, and dumped the remnants of their revelry in trashpiles called “middens.”
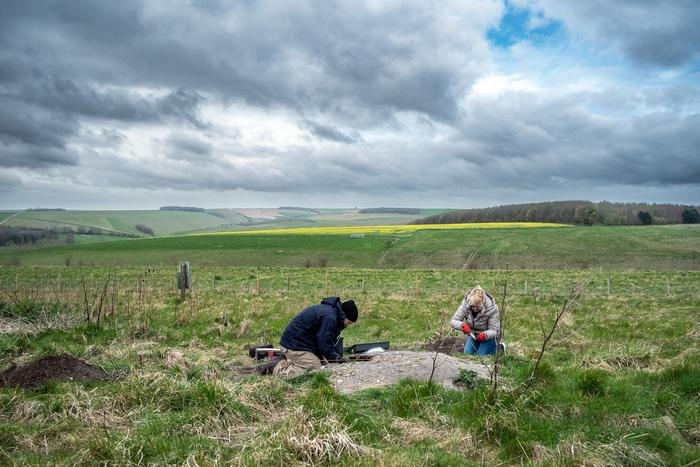

“These vast mounds of cultural debris represent the coming together of vast numbers of people and animals for feasts on a scale unparalleled in British prehistory,” said researchers led by Carmen Esposito of Cardiff University. “This study, the largest multi-isotope faunal dataset yet delivered in archaeology, has demonstrated that, despite their structural similarities, middens had diverse roles.”
"Given the proximity of all middens to rivers, it is likely that waterways played a role in the movement of people, objects and livestock,” the team added. “Overall, the research points to the dynamic networks that were anchored on feasting events during this period and the different, perhaps complementary, roles that different middens had at the Bronze Age-Iron Age transition.”
When in doubt—then as now—have a big party.
Thanks for reading! See you next week.