Hudson Institute lists Russia’s eight most fragile military arteries Ukraine could sever next to break the stalemate
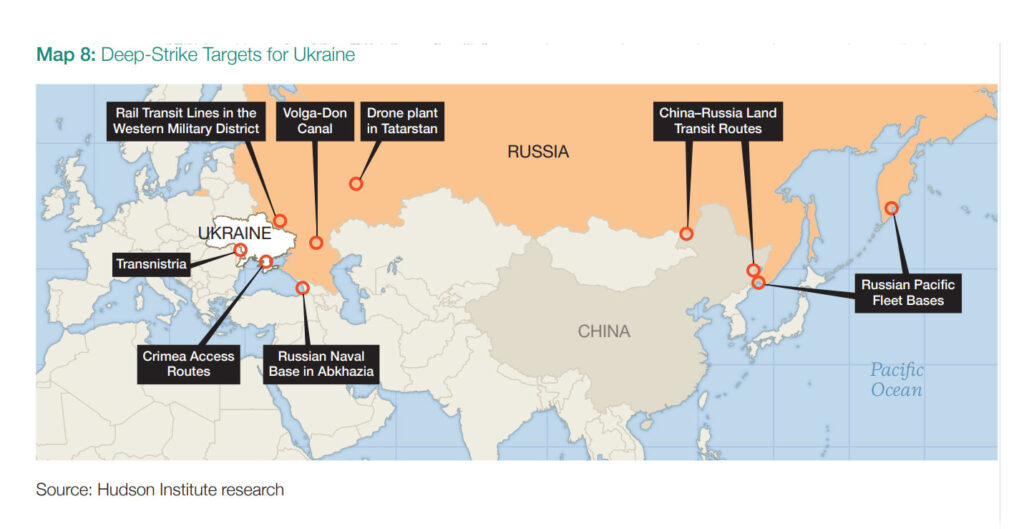
The Hudson Institute has identified eight critical targets across Russia and occupied territories that Ukraine could strike to destabilize Moscow’s war effort. The report, authored by Luke Coffey and Can Kasapoğlu and titled “Breaking the Stalemate: Russian Targets Ukraine Should Strike,” argues that sustained pressure on these chokepoints could undermine Russian logistics, weaken the Kremlin’s control over occupied areas.
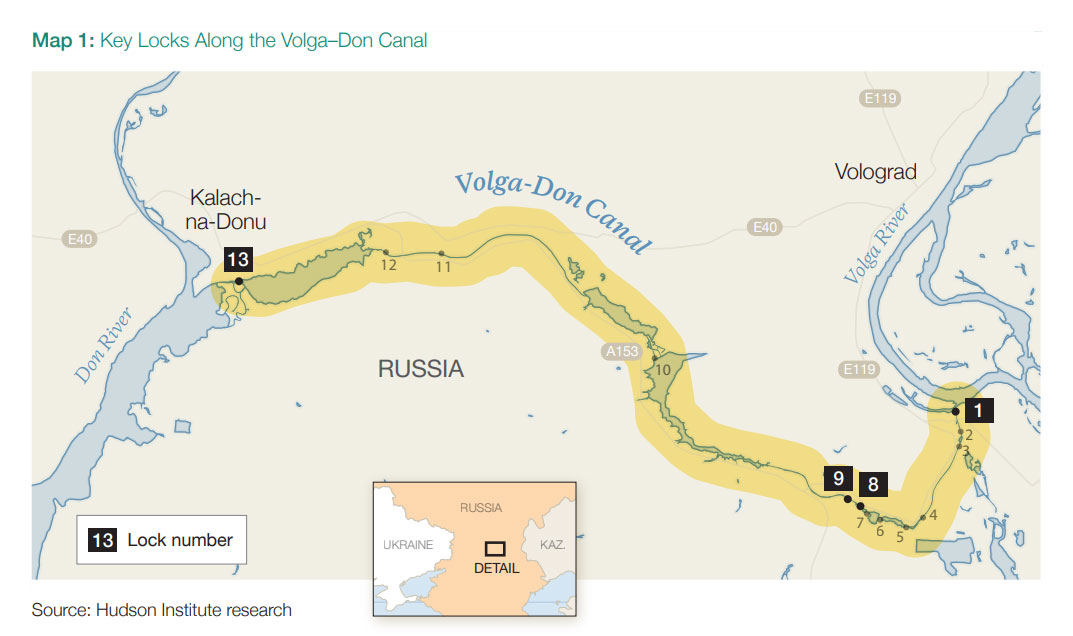
Volga–Don Canal
The Volga–Don Canal is a 63-mile waterway linking the Caspian and Black Seas. Russia uses it to move vessels from the Caspian Flotilla and to transport Iranian-supplied weapons. The Kremlin has committed $1 billion to modernize the canal, underscoring its importance. Analysts note that damaging Locks 8 and 9, which sit at the canal’s summit, could halt navigation and disrupt water flow, crippling east–west logistics and trade with Iran.
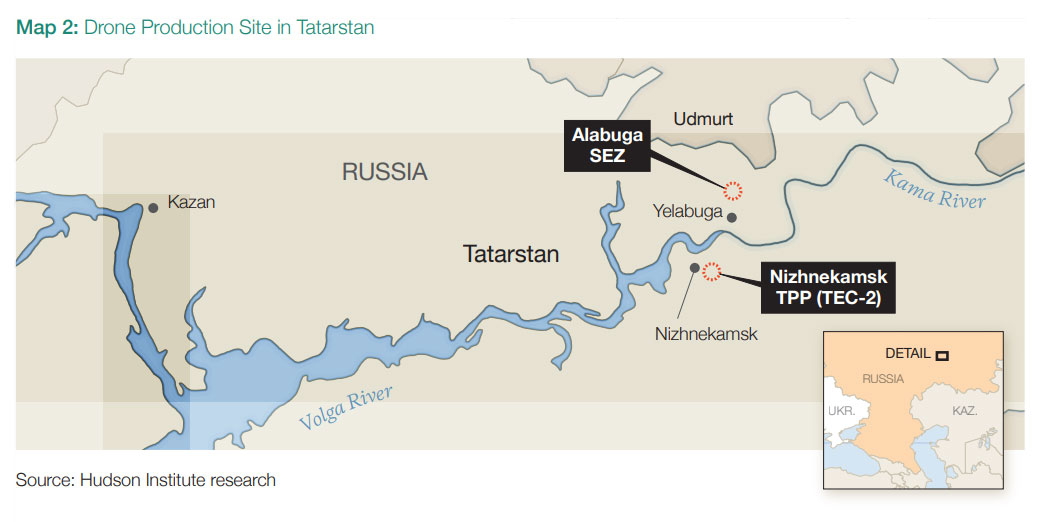
Shahed Drone Plant in Tatarstan
Located in the Alabuga Special Economic Zone, Russia’s main Shahed drone facility produces multiple variants with Iranian support.
Open-source reporting indicates that Russia’s Shahed drone plant in Tatarstan likely produces 170–190 drones per day. In June 2025 alone, Russia launched around 5,500 Shaheds against Ukrainian cities. Production could rise further, with estimates suggesting up to 2,000 drones per month by late 2025.

Ukraine’s GenStaff says its deep strikes have erased 4% of Russia’s GDP this year—42% of attacks targeted oil refineries (infographics)
The facility employs thousands, including foreign workers and students, raising civilian risks. The report suggests Ukraine could instead target the plant’s energy lifeline at the nearby Nizhnekamsk Thermal Power Plant to disrupt production indirectly.
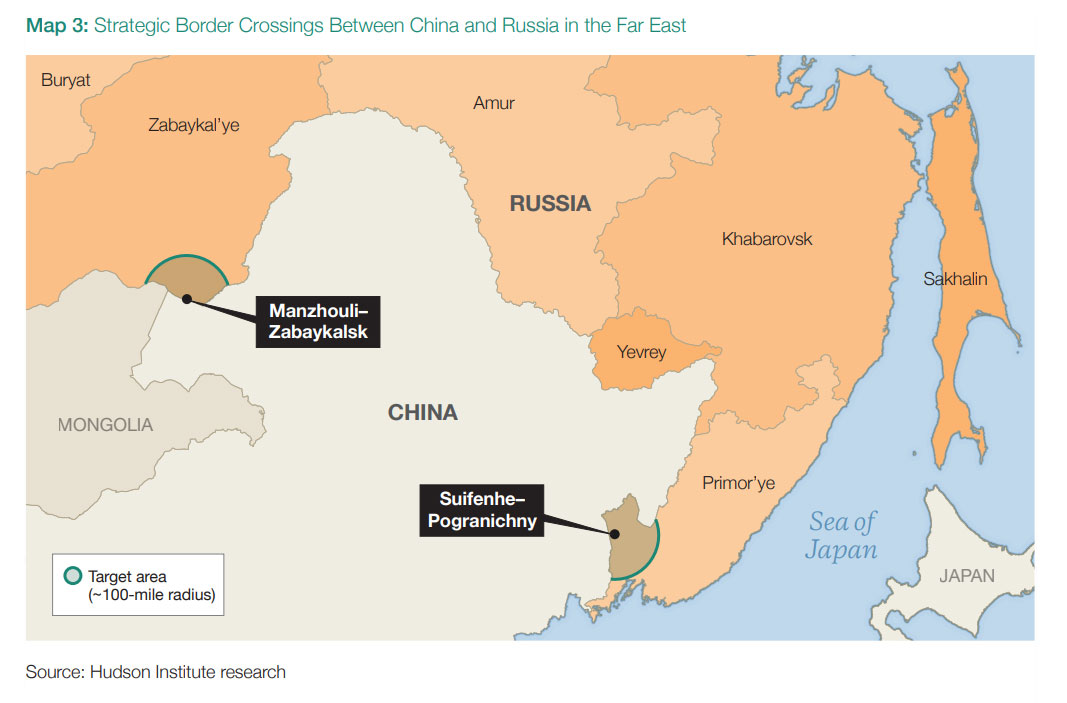
China–Russia Land Routes
Russia’s wartime dependence on Chinese imports has soared, reaching $240 billion annually. These include drones, optics, semiconductors, and weapon components. Around 90% of this trade crosses the border by rail through Manzhouli–Zabaykalsk and Suifenhe–Pogranichny. While directly striking at the crossings could be politically fraught, Hudson Institute identifies rail bridges and railyards within Russia as vulnerable chokepoints that, if disrupted, would slow the flow of critical dual-use goods
.
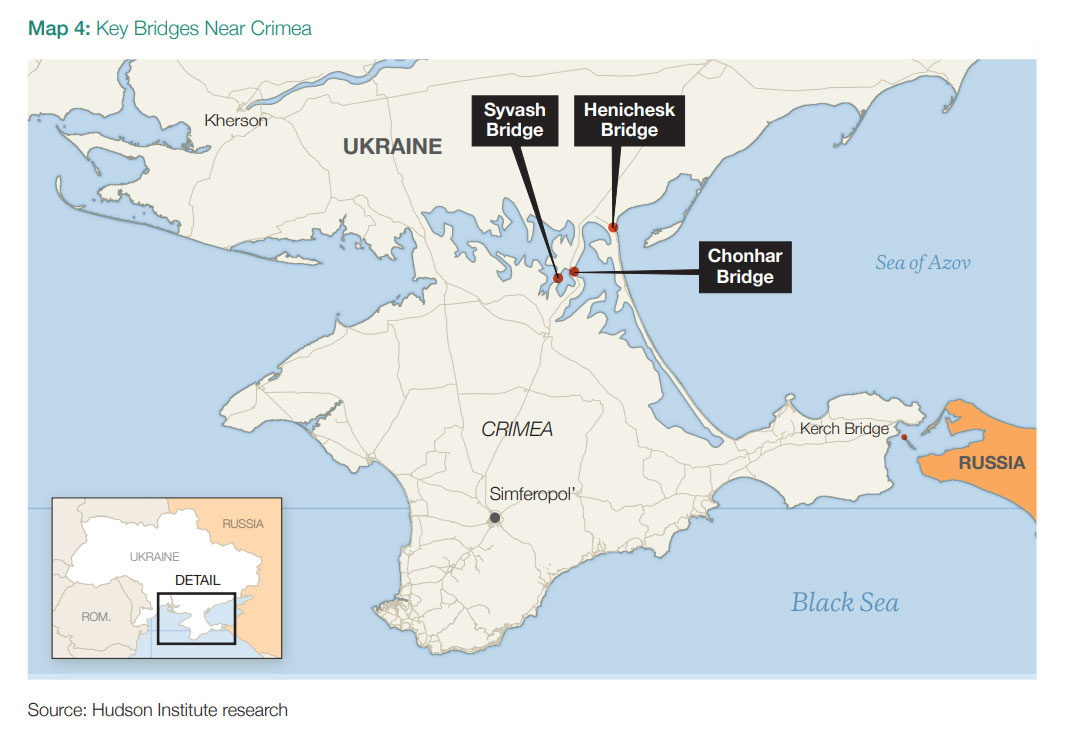
Crimea’s Access Routes
Crimea remains a central hub for Russia’s southern operations. The Kerch Bridge has been attacked and damaged three times, but never destroyed. The report stresses that Western-supplied long-range missiles, such as Germany’s Taurus, could finish the job. Analysts also highlight smaller but equally vital routes into Crimea: the Chonhar, Syvash, and Henichesk Bridges. These links connect the peninsula to Kherson Oblast and are more vulnerable to attack than Kerch. Severing them would drastically weaken Russian supply lines into occupied southern Ukraine.
Rail Bridges in Western Russia
Russia’s military depends heavily on rail, moving up to 30,000 tons of ammunition and fuel daily. Each division requires about 1,870 tons of cargo, with artillery munitions accounting for half. While trains in motion are difficult to strike, Hudson Institute stresses that rail bridges, transformers, and substations are fixed and exposed. Recent Ukrainian strikes in Samara and along the Oryol–Kursk line show this tactic is viable. Sustained attacks could cripple supply lines across the Russian heartland.

Three fires, one night: Ukraine hits refinery, military base, and railway in deep Russian strike (video)
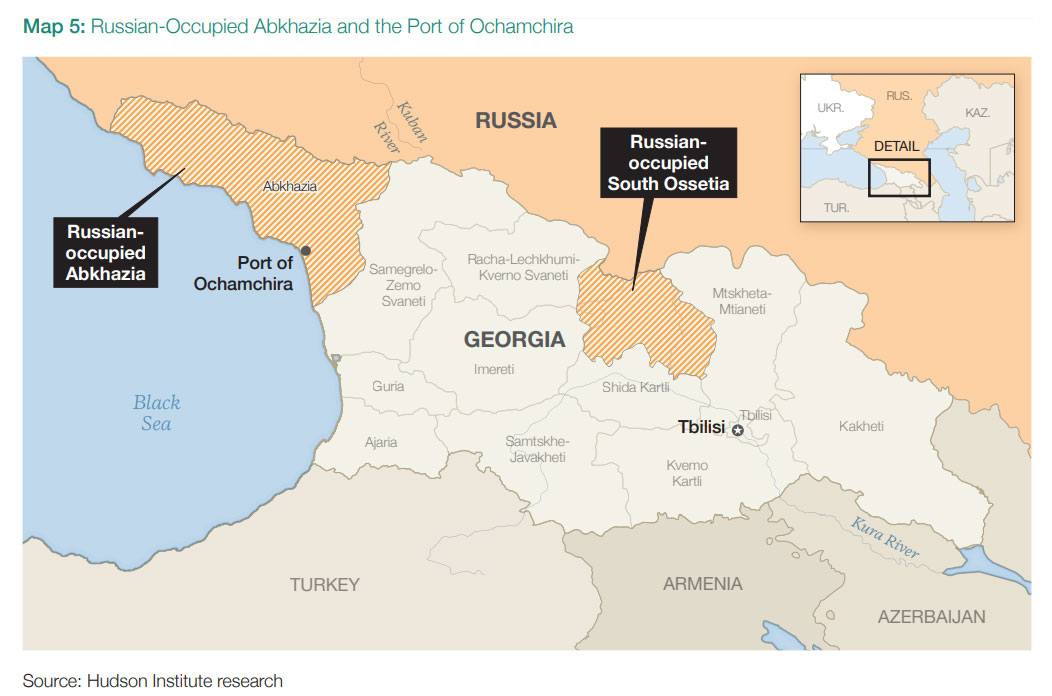
Emerging Russian Base in occupied Abkhazia
Moscow is shifting parts of its Black Sea Fleet to Abkhazia’s Ochamchire port, on occupied Georgian territory, after heavy losses in Crimea. The new base remains under construction and vulnerable. The coastline is exposed, infrastructure is weak, and supply routes rely on a single road and rail link with a bridge that forms a critical choke point. Hudson Institute concludes that striking early could delay or halt Russia’s efforts to diversify its naval footprint in the Black Sea.
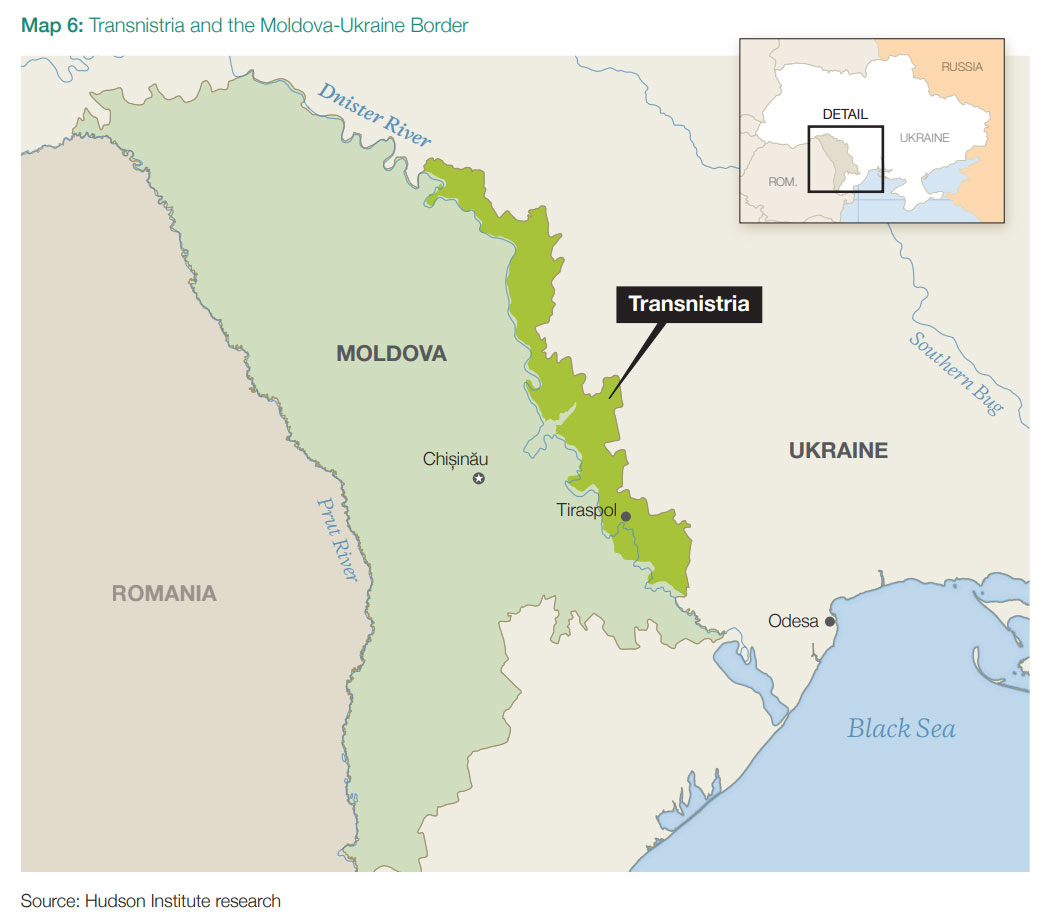
Transnistria
The Russian garrison in Moldova’s Transnistria enclave is another fragile point. About 1,500 troops remain there with outdated equipment and no realistic way to reinforce them. Ukraine, the report argues, could eliminate the pocket if necessary, relieving pressure on Odesa. But the analysis also warns that such a move would risk humanitarian fallout in Moldova and Romania, especially near the massive Cobasna ammunition depot.
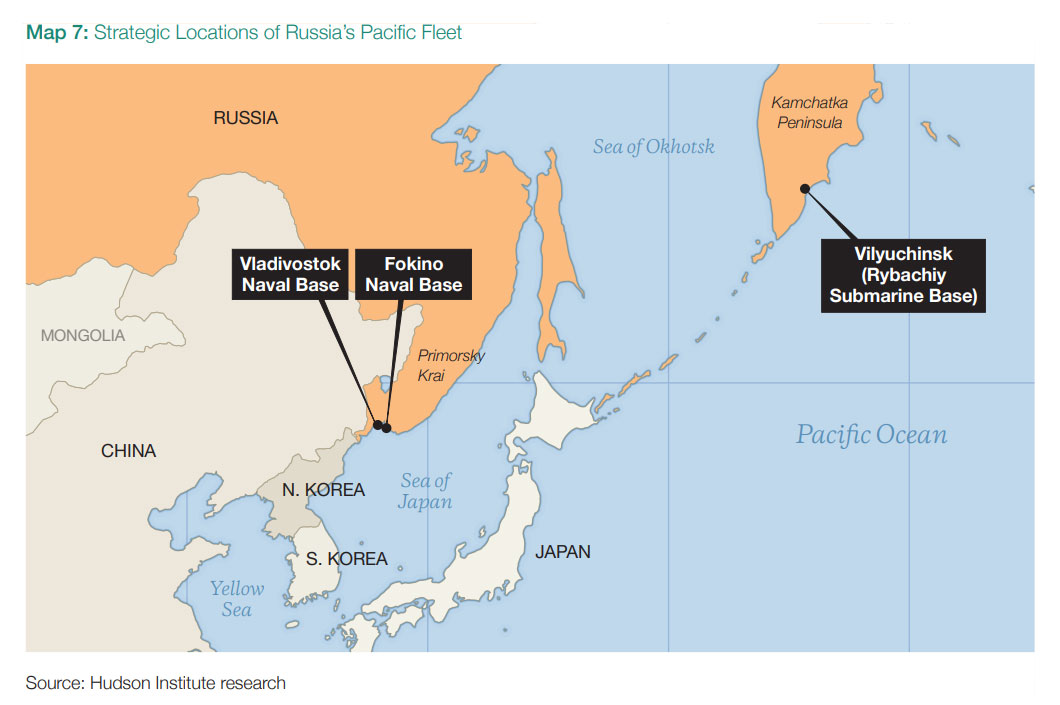
Russian Pacific Fleet Bases
Though far from the battlefield, Russia’s Pacific Fleet has quietly supported the war. It has transferred naval brigades to Ukraine and redeployed ships to the Black Sea. These distant bases lack the dense defenses seen in Crimea, making them potential targets. Analysts suggest Ukraine could adapt maritime drones to reach the area. Even limited strikes would force Moscow to disperse defenses and reconsider its global naval posture.
Read also
-
Ukraine strikes Russian Olya port in Astrakhan Oblast, targeting vessel with Iranian drone parts
-
Russia says 13 drones destroyed — but Syzran refinery burns and videos show fire raging at military-linked fuel plant
-
Satellite photos reveal what’s left of Russia’s key oil hub and prized radar in Crimea